Jul 09 2015
The Nebra Sky Disc — an astronomical Bronze Age treasure
Discovered in 1999, the European Bronze Age astronomical artifact known as the Nebra Sky Disc was nearly lost to the black market, but fortunately found itself in the hands of the scientific community. It is now on display at the State Museum of Prehistory in Halle, Germany.
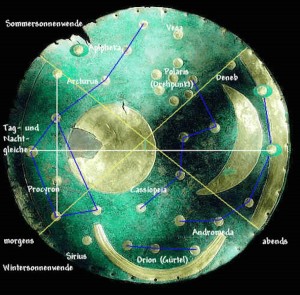
Dated to circa 1600 BCE, the bronze and gold-emblazoned disc contains a graphical representation of the sun, moon, and the constellations Andromeda and Cassiopeia, among other celestial objects of agricultural and calendrical importance, including the Pleiades.
The astronomical sophistication it demonstrates is remarkable. Astronomer Ralph Hansen has determined that the disc served to coordinate the solar and lunar cycles for agricultural purposes.
Perhaps just as important is the glimpse it offers into the astral religion of the Bronze age in Northern Europe. This is supported by Hansen’s research, which demonstrated a striking parallel to a rule of intercalation (i.e., adding a thirteenth month to the year) related to the lunar crescent found in the Babylonian MUL.APIN, dating a thousand years later, to the seventh-sixth centuries BCE. According to Hansen, the intercalary month would be added every two to three years when the position of the Pleiades in the night sky matched its position on the Nebra sky disc. However, according to archaeologist Harald Meller of the State Museum for Prehistory at Halle (who was involved in the recovery of the disc), later layers suggest that at least some of its astronomical function was eventually lost, and “that in the end the disk became a cult object.” Astronomers Emilia Pasztor and Curt Roslund go even further, stating that it more likely served a religious purpose for the Northern Bronze Age European elite, including chiefs and shamans. [The full article, in Antiquity 01/2007; 81 (312):267-78, may be accessed here.]
In 2013, the Nebra sky disc was added to UNESCO’s ‘Memory of the World’ Register.